In high-performance football, monitoring player responses to matches is essential for managing load, guiding recovery, and minimizing injury risk. A recent study by Mohr, Bishop & Dal Pupo (2025) published in Sport Sciences for Healthadds strong evidence that countermovement jump (CMJ) metrics are sensitive markers of post-match neuromuscular fatigue.
The study tracked 30 professional soccer players who performed CMJ tests on MD-1 (one day before match) und MD+2 (two days after match) throughout a full season. What they found was consistent: jump height and RSI-mod (Reactive Strength Index modified) significantly declined on MD+2, especially for players with high match exposure (>69 minutes played).
Key Findings:
- CMJ height und RSI-mod drop after matches, especially in those playing longer durations.
- These markers are reliable tools for assessing post-match fatigue and load tolerance.
- Fatigue levels vary by minutes played, which supports the need for individualized recovery strategies.
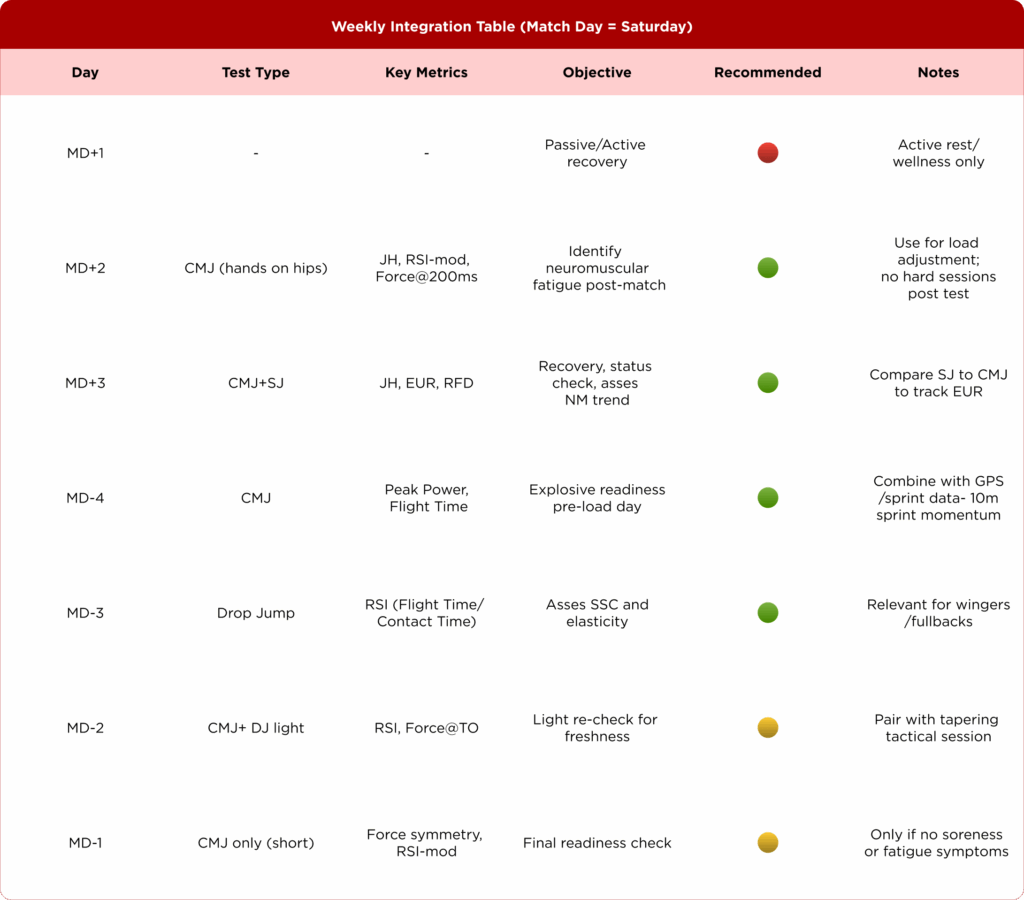
CMJ in the Weekly Structure – A Realistic Application
At our teams , we’ve seen similar trends when monitoring our teams. While full testing batteries have their place (typically on MD-3 or MD-4), brief CMJ screens can act as early flags for fatigue and readiness.
However, it’s important to clarify: this is not a substitute for a proper testing day. Instead, it’s a quick data collection opportunity to check how players are responding to game loads.
And remember: neuromuscular data is only one piece of the puzzle. To fully understand a player’s readiness and recovery, combine CMJ outcomes with:
- Subjective feedback (e.g., wellness scores)
- Cardiac responses (HRV, resting HR)
- Pulmonary markers (breathing rate, SpO₂ if available)
- Movement and training load (via GPS / accelerometers)
Reference:
Mohr, P. A., Bishop, C., & Dal Pupo, J. (2025). Variation in countermovement jump metrics following competitive soccer matches throughout a season in professional players. Sport Sciences for Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-025-01042-3



